Introducing AT-001

AT-001 is an innovative, oral treatment with no observed side effects. It is designed to address rare and common forms of dementia caused by harmful protein accumulations, specifically amyloid-induced angiopathy. Its mechanism of action is focused on the disruption and dissolution of harmful protein clusters, or oligomers, within the brain. This is achieved by reducing disulfide bonds, the structural elements that maintain these detrimental protein structures.
AT-001 breaks down protein aggregates
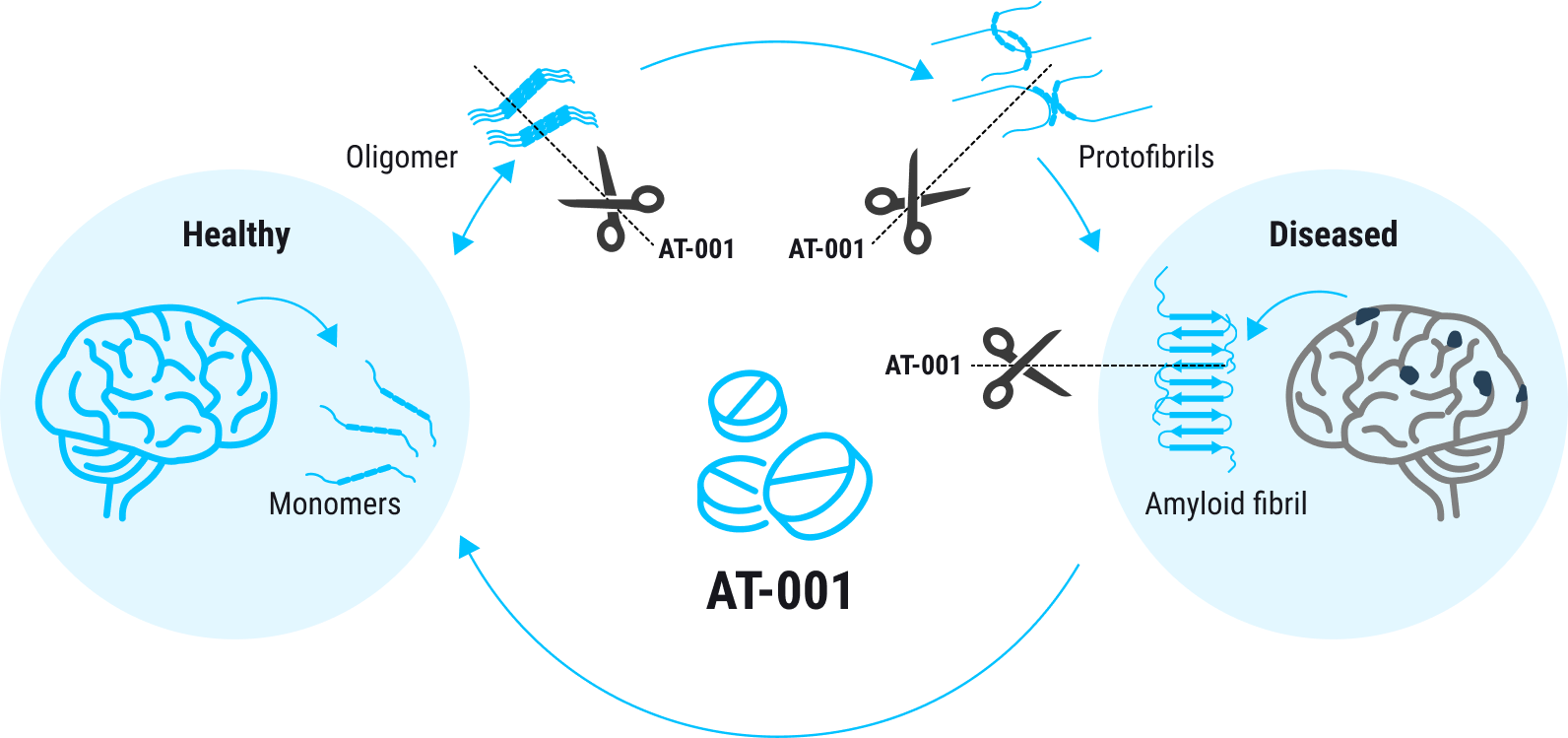
Results from our phase IIa clinical trial, which investigated a particular mutation found in Iceland, have shown positive outcomes. Our data demonstrates AT-001’s potential in preventing the rapid accumulation of amyloid proteins, thereby reducing the risk of stroke and early dementia. Looking ahead, AT-001 aims not just to slow or halt the progression of rare and common forms of dementia, but to potentially delay its onset or even reverse its course. We have launched our phase IIb/III registration study, following an approval from the European Medicines Agency (EMA).
1
Addressing rare forms: AT-001 combats rare hereditary forms of dementia such as Hereditary Cystatin C Amyloid Angiopathy (HCCAA) and related Cerebral Amyloid Angiopathies (CAAs), which account for an estimated 5% of all dementia cases.
2
Tackling Alzheimer’s: AT-001 also tackles the widespread challenge of Alzheimer’s disease, responsible for 60-70% of all dementia instances.
3
Innovative intervention: AT-001’s distinctive mechanism of action sets it apart. By disrupting toxic protein aggregates and inhibiting their formation, it provides a dual approach to preventing brain damage and onset of dementia.
Hope in an
unexpected place
Katrín Björk Guðjónsdóttir experienced multiple strokes by the age of 21 due to a rare familial genetic condition.
Read her story and find out how her personal triumph became the catalyst for the development of AT-001.

AT-001 has the potential to totally transform the AD segment in the neurological disorder drugs market […]. If fully validated, AT-001 could displace or potentially remove […] current offerings. Given the dementia forecast cost of €2.8 trillion in 2030, success with AT-001 would mean massive savings due to less DALYs (Disability-Adjusted Life Years) and less premature deaths or lower time spent caring for dementia patients by carers.
– EIC jury member.
Accelerating treatment for millions of people
Dementia and Alzheimer’s disease present urgent health challenges worldwide. With an aging population, the incidence of these conditions is rising dramatically, placing a significant burden on healthcare systems and families.
The World Health Organization (WHO) estimates that over 55 million people have dementia globally, with nearly 10 million new cases diagnosed every year. In 2030, dementia-related costs are expected to reach $2.8 trillion. The Alzheimer’s Association estimates that the total cost of care for individuals with Alzheimer’s and other dementias in the United States will be $345 billion in 2023.

55 million people have dementia worldwide

Without effective treatments, the cost associated with dementia is forecasted to reach €2.8 trillion in 2030.

10 million new cases are
diagnosed each year
Dementia and Alzheimer’s disease present significant challenges for individuals and their families.
These conditions are progressive and degenerative, leading to a decline in cognitive and functional abilities over time. Some of the challenges faced by people with dementia and Alzheimer’s include:
Behavioral
changes
One of the hallmark symptoms of dementia and Alzheimer’s is memory loss. Individuals may struggle to remember recent events or to retain new information, making it difficult to learn and engage in activities of daily living.
Communication
difficulties
As the disease progresses, individuals may have difficulty communicating effectively, leading to frustration and isolation. They may struggle to find the right words, or to understand what others are saying, leading to misunderstandings and social withdrawal.
Memory loss
As the disease progresses, individuals may experience changes in mood and behavior, including agitation, aggression, and depression. These changes can be distressing for both the individual and their caregivers.
Caregiver burden
Caring for someone with dementia or Alzheimer’s can be challenging and demanding, both emotionally and physically. Caregivers may experience stress, burnout, and financial strain, and may struggle to balance their caregiving responsibilities with other obligations.
Social isolation
People with dementia and Alzheimer’s may experience social isolation and a loss of independence as their condition progresses. They may be unable to participate in activities they once enjoyed, and may struggle to maintain social connections.
Increased healthcare costs
Dementia and Alzheimer’s disease are associated with increased healthcare costs, including hospitalizations, long-term care, and medication expenses. These costs can be a significant burden for individuals and families, as well as healthcare systems.